Coaxial cable and assemblies
Coaxial cables have been around since the beginning of the 20th century and have been used to carry high-frequency electrical signals with low losses. They are commonly used in relaying video, audio, and other signals in a variety of different applications. They are used in telephone cable lines, T.V. cable connections, connection to radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas, computer network connections, amongst other applications.
Jyebao is a leading manufacturer of coaxial cables. They manufactures diffrent types of coaxial cables with different varieties of connectors at either ends of the cable. Please have a look through the Jyebao website https://www.jyebao.com.tw/ for further product information.
Parts of the coaxial cable:
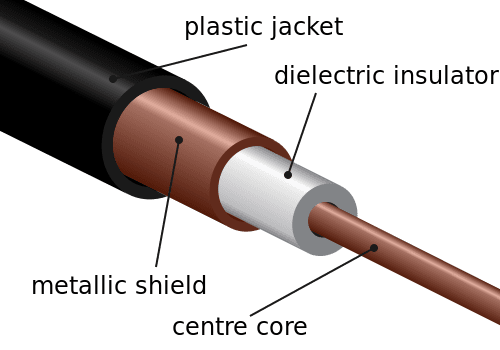
Coaxial cable has a central conductor which primarily transmits the RF signal. This conductor is usually made up of solid copper, stranded copper, or copper-plated steel wire. The conductor is surrounded by a dielectric insulator that minimises the loss of the signal. This dielectric insulator is protected by one to four layers of metallic braid or metallic tape that protects the cable from electro magnetic interference. This metallic braid is in turn covered by an outer insulating plastic jacket.
Types of coaxial cable:
Coaxial cables are primarily categorised based on the materials that make up the cable. A detailed description of the following categories is given below.
Flexible coaxial cable:
As the name suggests, this coaxial cable can flex and move to suit the geometry and configuration of the application. This cable typically consists of solid metallic wire as an inner core, surrounded by a flexible polymer that serves as a dielectric, and an outer jacket. To make this cable more flexible, the solid metallic wire could be swapped for a stranded wire and the polymer dielectric can be switched with a polyethylene dielectric foam.
Flexible coaxial cables were initially designed for military purposes; however, they are now used in data transmission, relaying videos and wireless connectivity. There are a wide range of connectors, such as BNC, SMA, N-type, and TNC can be used on either ends of this cable, thus making it perfect for low and mid-frequency application.

Flexible cable with SMA plug to SMA plug
Semi-rigid coaxial cable:
Semi-rigid coaxial cable is known for its shielding effectiveness and for its high-frequency performance. This perfromance is attributed to the presence of a dielectric polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and a solid copper outer sheath. This cable is commonly used in high-frequency internal applications. It is commonly used in telemetry applications, radar equipment, amplifiers, and microwave products. The semi-rigid cables can be atached to a wide range of connectors, such as SMA, TNC, or MCX, at either end.

Semi-rigid cable with SMA plug to SMA plug
Conformable /Formable coaxial cable:
Conformable cable, also known as formable cable, is known for its ability to be reshaped to ideal configuration by hand and does not require specialised tools. This cable has a flexible metal sheath that is surrounded by a rigid copper outer covering. Conformable cables are usually used to replace semi-rigid cables.

Conformable cable with SMA plug to SMA plug
Low loss coaxial cable:
Low loss cable is known for its low loss of signal which could be attributed to its efficient and reliable shielding. This cable is known for its high performance and flexibility in 50-ohm configuration. This cable offers a tight bend radius and is ideal for outdoor applications and can be used in outdoor applications, such as antenna cable jumpers. This cable can use a variety of connectors, such as BNC, TNC, SMA, and N-type connectors at either end.
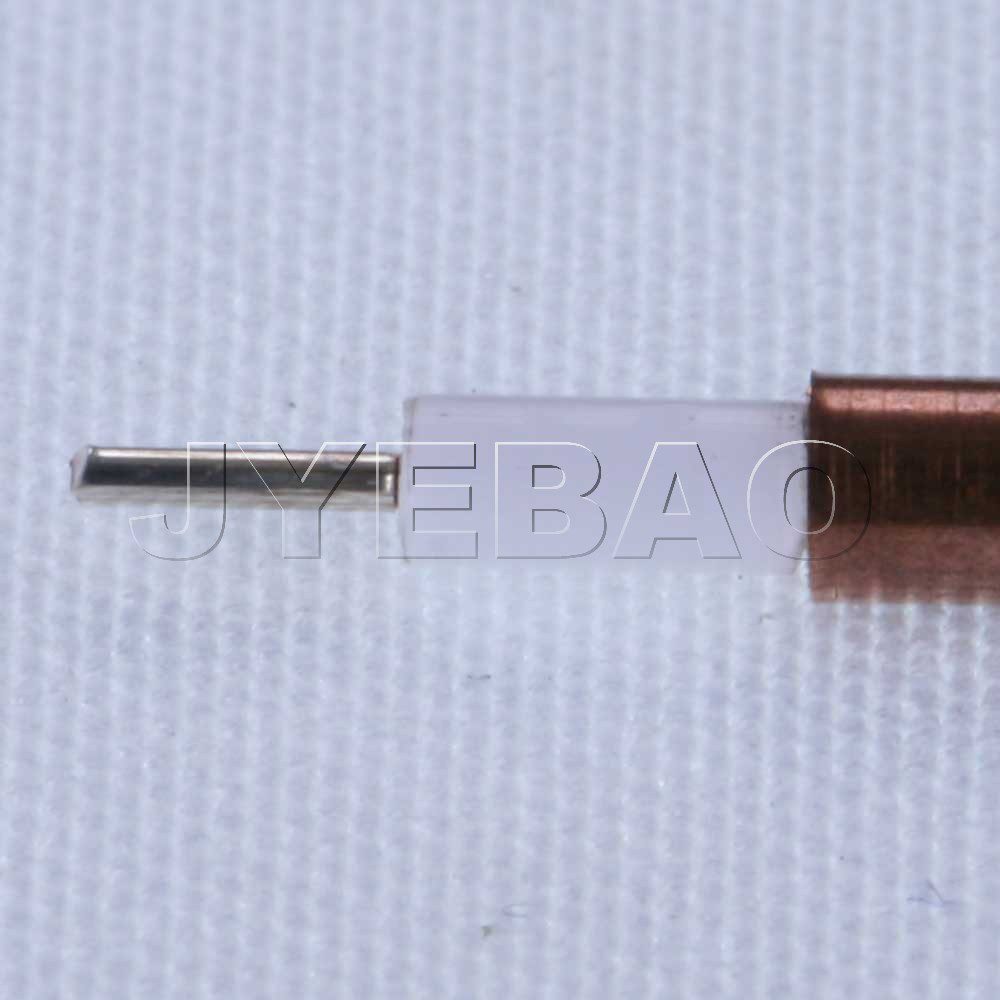

50-Ohm low loss cable
Hard line coaxial cable:
Hard line coaxial cable is larger in diameter (typically between 12 to 13 mm in diameter) compared to other RF coaxial cables and is used in high-strength signal transmission. Its central conductor is made of copper, silver, aluminum, or steel central conductor. To prevent the accumulation of moisture and arcing pressurised nitrogen is commonly used in this cable. It is used to transmit signals over long distances over 300 to 400 feet and are generally suspended from telephone poles.
Rigid coaxial cable:
The rigid coaxial cable is characterized by its rigid line and has two concentric copper tube at regular intervals to support the length of the cable. This cable also has a PTFE disk insulator. The rigid cables are sold in straight sections and come with 45 and 90 couplings that could provide bends in the transmission lines.
Twinaxial coaxial cable:
This coaxial cable is unique as it has two central core conductors that is surrounded by a dielectric and an outer sheath. This cable is often seen in video applications and is used in low frequency digital applications. The twinaxial cable is known for its reduced low cable loss, greater protection from ground loops and capacitive fields, and reduction in low-frequency magnetic noise.
Apart from the above mentioned general catogoes, coaxial cables are also characteristics based on cable thickness (also referred to as the gauge), and impedance.
Gauge of the coaxial cable:
The gauge of the coaxial cable is usually quantified by radio guide measurement also known as RG number. The higher the RG number the thinner the central conductor is expected to be. The most popular type of coaxial cables are RG-6, RG-11, and RG-59.
RG-6 cables:
RG-6 cables have large conductors and thick dielectric insulation. They have different layers of shielding that enable them to transmit the signal more effectively. These cables are thin and can be easily installed in walls or ceilings.
RG-59 cables:
RG-59 cables have a thinner central conductor compared to RG-6 cables. They are the ideal choice for short runs and low-frequency transmissions and are commonly used in domestic situations.
RG-11 cables:
RG-11 cables are thicker than most other coaxial cables and can easily be identified. Its offers lower attenuation levels than RG-6 or RG-59 and are hence used to carry data over long distances.
Impedance of coaxial cable:
Based on the impedance, the coaxial cables can be categorised into two groups: one with an impedance of 75 ohms and another with an impedance of 50 ohms. Coaxial cables with an impedance of 75 Ohm are generally used for transmitting video signals while those with an impedance of 50 ohms are used to transferring data and wireless communication.
